Database Structure – Entity Relationship Diagram
Aedon has a robust database structure to handle the complex nature of an accounting solution.
At its core, Salesforce Database is a cloud-based, relational database management system (RDBMS) designed specifically for the unique needs of sales, marketing, and customer service teams. This database plays a pivotal role in the Salesforce ecosystem, underpinning the suite of applications that empower businesses to streamline operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive revenue growth.
Aedon contains 174 custom objects in the managed package and there are 22 types of Transaction that generate postings or Ledger Entries. Therefore, the diagram below is a necessarily simplified version using the Sales Invoice as an example transaction.
Simplified Entity Relationship Diagram
The diagrams reads from left to right.
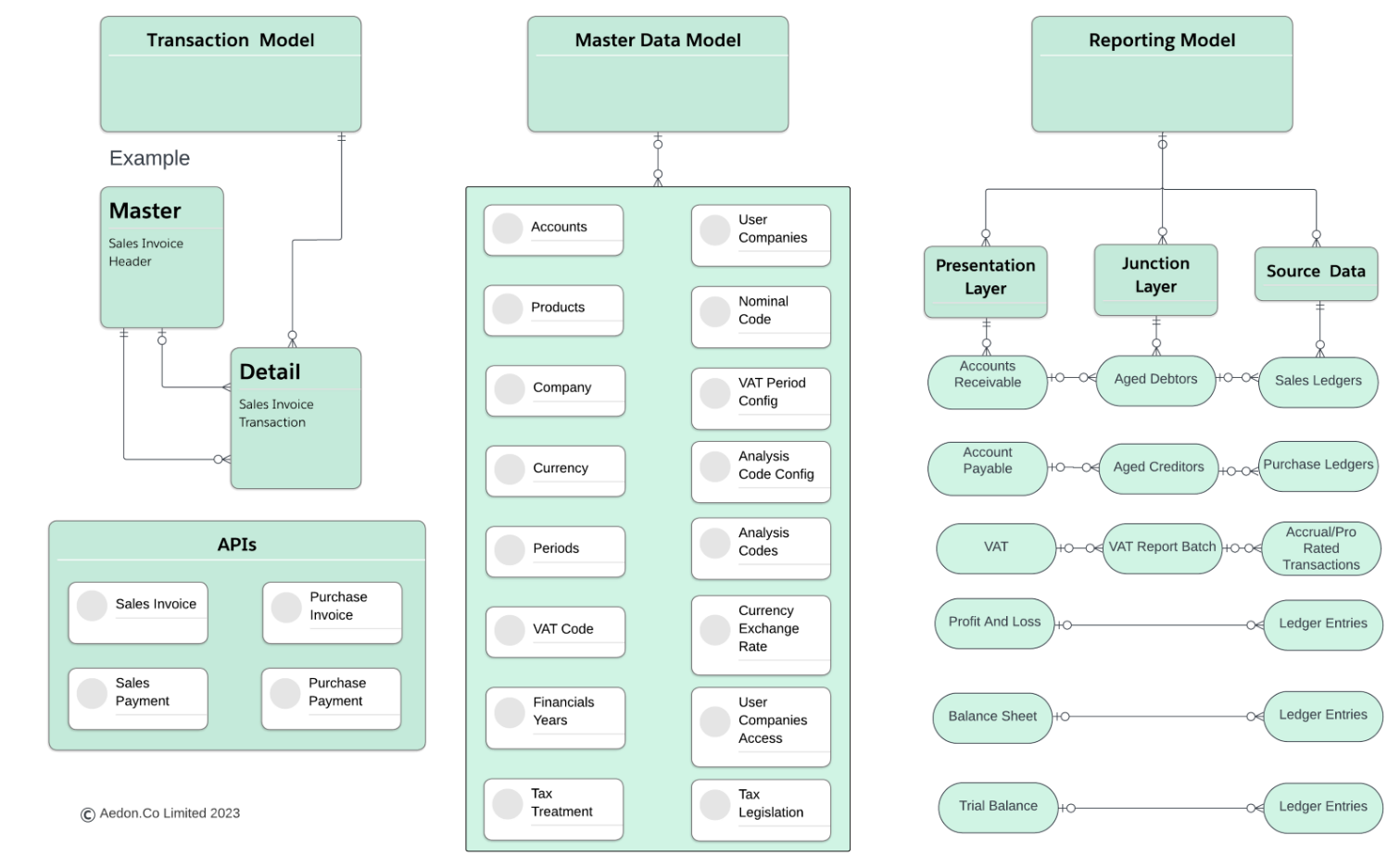
Transaction Model
The Transactional objects are always defined as a Master-Detail pair with a Header and Transaction Item to accommodate the accounting transactional data like invoices, credit notes and other crucial transactions.
Master Data Model
The Master Data objects hold data like Tax Codes, Nominal Codes, Accounts, Currency, Currency Exchange Rates, and other data that is not changed very frequently.
Reporting Model
The Reporting Model has three components: the Reporting Layer, the Junction Layer, and the Source Data.
Presentation Layer
Accounting reports are very complex to produce hence Aedon will transform the raw data held in all transaction objects to make it presentable for the users. Admins can leverage these objects to build their own representations of the data using standard Salesforce report builder.
Junction Objects
Aedon uses a wide range of junction objects to transform the data for all the financial reports that is offered out of the box in the accounting package. These junction objects hold the transformed data from the database and act as a bridge between the Transactional objects and the reporting objects.
Source Data
Most reports in Aedon are produced using the Ledger Entries, but there are two exceptions:
- Accounts Receivable & Payable which use Sales and Purchase Ledger Entries
- VAT reports which use the Accrual/Pro-Rated Transactions.
Key Benefits of the Aedon Database powered by Salesforce.
- Scalability: Salesforce Database is highly scalable, allowing businesses to accommodate growing data volumes and adapt to changing needs effortlessly. This scalability ensures that your system can evolve with your organization.
- Data Security: Data security is paramount in the Salesforce Database. It employs robust security measures and encryption to protect sensitive information, meeting industry and compliance standards.
- Customization: Organizations can tailor their database schema to suit their specific requirements. Custom objects, fields, and relationships enable businesses to capture and organize data in a way that aligns with their unique processes.
- Integration: Salesforce Database seamlessly integrates with various Salesforce products, as well as external systems and applications, facilitating a holistic view of customer interactions and business operations.
- Automation: With the power of Salesforce Automation, businesses can automate routine tasks, workflows, and data updates, freeing up valuable time for sales and support teams to focus on building relationships and delivering exceptional customer experiences.
- Analytics: Leveraging the Salesforce Database, organizations can harness the power of data analytics and reporting to gain deep insights into their operations, customer behaviour, and sales performance, enabling data-driven decision-making.




















